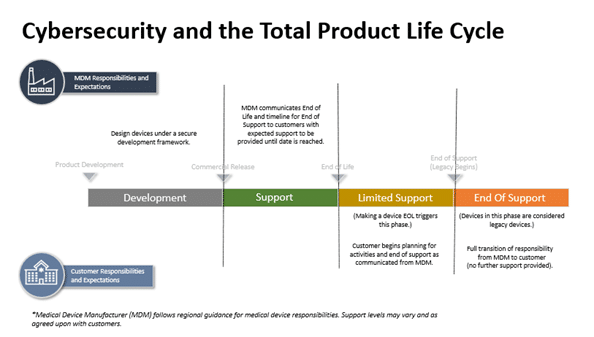
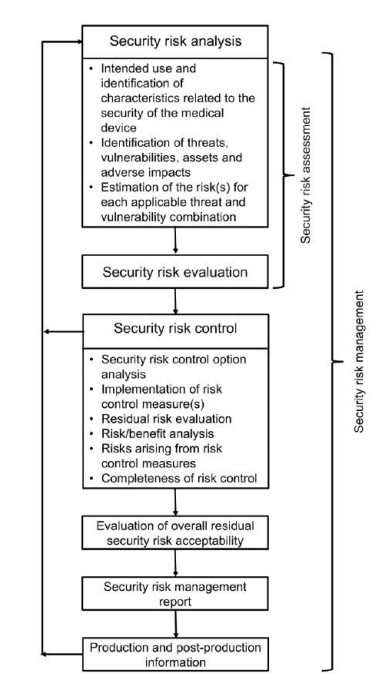
Among the emerging topics of interest to the life science industry, quality culture, quality metrics, and data integrity are in the spotlight due to changes from the COVID-19 pandemic. Regulatory authorities strive to stay on top of the latest challenges in quality assurance and compliance facing medical device and pharmaceutical firms.
Regulatory Compliance Associates® understands that data integrity is important for keeping and maintaining accurate data to protect your data’s trustworthiness. This ensures everything else built on that data is trustworthy as well. We’ll explore why quality culture and data integrity are important and what permanent changes have occurred in the wake of the pandemic.
Need help improving your Quality Culture? Contact Us Now →
How Quality Culture Is Linked to Data Integrity
It’s essential to understand the ways quality culture is linked to data integrity. Regulators have delineated a clear link between the veracity of data generated by a company and its culture. Future regulatory audits to determine an organization’s health may focus on obtaining information about the company’s quality culture and subsequent data. It’s vital to for companies to acknowledge this relationship so they can identify vulnerabilities, perform necessary risk assessments and remediate risks before an inspection.
An Increased Emphasis on Data Integrity
It’s easier to keep a vigilant eye on data when everyone works from the same locations. However, with more people working from home, maintaining quality culture practices to control data integrity is imperative and challenging. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is drawing parallels between compliance with data integrity regulations and an organization’s overall culture.
The FDA wants companies to maintain a quality culture that is integrated throughout the organization. The more developed and established an organization’s quality culture, the more reliable the data.
Ensuring data integrity compliance can benefit a company in the following ways:
- Fewer supply chain interruptions
- Less rework needed
- Reduced financial risk
- Increased compliance
- Improved operational performance and productivity
Transitions to Electronic Systems
As a result of the pandemic, more companies are switching from paper-based to electronic systems. This migration to electronic data systems poses certain challenges to any organization.
Companies need to have the necessary resources and technical expertise to make sure the electronic systems maintain data integrity concepts. Organizations must be able to provide proof of their compliance supported by an audit trail of their work.
Auditing Process Changes Resulting from the COVID-19 Pandemic
The auditing process may change in many ways as a result of the pandemic:
- Virtual audits are likely to become more common.
- Companies will need to ensure systems are secure and files are organized.
- Companies will have to maintain data integrity in their electronic systems so they can use those systems to transfer data to regulatory auditors.